Composting stands as a vital practice in our quest for sustainability, transforming organic waste into rich soil while simultaneously promoting environmental health. This process not only reduces the volume of waste destined for landfills but also enhances the quality of our soil, leading to greater biodiversity. By understanding the intricate components of compost and their contributions to ecological well-being, we can appreciate the profound impact composting has on our planet.
As more communities embrace composting, it becomes essential to communicate its benefits effectively. Through awareness and education, we can inspire individuals to adopt this environmentally friendly practice, fostering a collective effort towards waste reduction and soil enhancement.
Introduction to Composting

Composting is a natural process that transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments. This essential practice not only reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills but also enhances soil health, promotes biodiversity, and mitigates climate change. Understanding the intricacies of composting reveals its significance in sustainable waste management and environmental stewardship.The composting process begins with the collection of organic materials, which include kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable substances.
These materials undergo a decomposition process facilitated by microorganisms, fungi, and insects. Over time, these organisms break down the organic matter, resulting in compost—a dark, earthy substance that enriches soil and supports plant growth. The significance of composting lies in its ability to recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, thereby reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers and minimizing pollution.
Components of Compost and Their Environmental Benefits
The components of compost play a pivotal role in its effectiveness and environmental impact. A successful compost pile typically consists of a balanced mix of green materials, brown materials, water, and air.Green materials, such as fruit and vegetable scraps, grass clippings, and coffee grounds, are rich in nitrogen. Brown materials, including dried leaves, straw, and cardboard, provide carbon. The combination of these elements is crucial for maintaining an optimal balance, which promotes efficient decomposition.
Here are the primary components of compost:
- Green Materials: These materials contribute nitrogen, essential for the growth of microorganisms that decompose the organic matter.
- Brown Materials: These provide carbon, which serves as an energy source for microbes and helps maintain the composting process’s temperature.
- Water: Moisture is essential for microbial activity, facilitating the breakdown of organic matter.
- Air: Adequate aeration prevents anaerobic conditions, ensuring that the decomposition occurs efficiently and without unpleasant odors.
The environmental benefits of composting are substantial. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), approximately 30% of what we throw away can be composted. By diverting organic waste from landfills, composting significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane, which is produced when organic matter decomposes anaerobically in landfills. Composting also improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and increases biodiversity in soil ecosystems.Statistics reveal the impact of composting on waste reduction.
In the United States alone, it is estimated that composting prevented the release of over 1.8 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent in 2018. This figure underscores composting’s role as a viable solution for waste management and climate change mitigation, demonstrating its importance in cultivating a sustainable future.
Environmental Benefits of Composting
Composting is a transformative practice that not only benefits individual gardeners but also has profound implications for the environment. By diverting organic waste from landfills, composting plays a critical role in reducing pollution and enhancing soil health. This section will delve into the various environmental advantages of composting, highlighting its significance in waste management, soil improvement, and water conservation.
Reduction of Landfill Waste and Methane Emissions
Composting significantly decreases the volume of organic materials that are sent to landfills. When organic waste decomposes in landfills, it generates methane, a greenhouse gas that is 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. By composting food scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials, individuals and communities can effectively reduce landfill contributions and associated methane emissions.
- In the United States, approximately 30% of the waste sent to landfills consists of organic materials that could be composted.
- Composting just one ton of organic waste can prevent the release of up to 0.75 tons of carbon dioxide equivalents, a crucial benefit in the fight against climate change.
“Diverting organic waste from landfills can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a healthier planet.”
Impact on Soil Health and Biodiversity
The introduction of compost into the soil has a multitude of benefits. Compost enriches the soil with essential nutrients, improves structure, and enhances its ability to retain moisture, thereby fostering healthier plant growth and enhancing biodiversity.
- Compost provides a rich source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, vital for plant development.
- The application of compost can increase soil microbial activity, promoting a diverse ecosystem that supports beneficial microorganisms and insects.
These benefits not only improve agricultural productivity but also contribute to the resilience of ecosystems, making them better equipped to withstand environmental stresses.
Conservation of Water and Improvement of Water Quality
Composting plays a crucial role in water conservation efforts. By enhancing soil structure, compost improves the soil’s ability to retain moisture, reducing the need for irrigation. Moreover, composted soil can filter and purify water, preventing pollutants from entering waterways.
- Adding compost to gardens can reduce water usage by up to 50%, depending on the soil type and climate.
- Healthy, compost-enriched soil can help prevent erosion and sediment runoff, leading to improved water quality in local streams and rivers.
“Utilizing compost in landscaping and gardening not only conserves water but also protects water quality by acting as a natural filter.”
Educating Others About Composting

Educating communities about composting is essential to fostering sustainable environmental practices. By sharing knowledge and providing resources, individuals can be empowered to contribute to waste reduction and soil health through composting initiatives. The following sections detail effective methods for teaching composting, designing impactful workshops, and engaging schools and local organizations in composting efforts.
Effective Methods for Teaching Composting to Communities
Implementing effective educational strategies can significantly enhance community understanding and participation in composting. Below are several methods that can be utilized to teach composting effectively:
- Demonstration Events: Organizing live demonstrations where community members can see composting in action helps demystify the process and encourages participation.
- Informational Workshops: Conducting workshops with knowledgeable speakers can provide insights into composting benefits and techniques, catering to various skill levels.
- Distribution of Educational Materials: Creating easy-to-read brochures, infographics, and online resources can help disseminate information about composting processes and benefits.
- Utilizing Social Media: Engaging with the community through social media platforms can increase awareness and share success stories about local composting initiatives.
- Partnering with Local Experts: Collaborating with local gardening experts or environmental organizations can lend credibility and attract participants to educational events.
Designing a Workshop Focused on the Benefits of Composting
A well-structured workshop can significantly inform participants about composting and its environmental advantages. Key elements of an effective workshop include:
- Workshop Objective: Clearly define the purpose, such as promoting sustainable waste management practices through composting.
- Content Artikel: Include topics such as composting basics, types of composting, benefits to the environment, and practical steps for starting a compost pile.
- Hands-on Activities: Incorporate activities such as preparing compost bins, identifying compostable materials, or even starting a small compost pile on-site.
- Resource Material: Provide participants with handouts summarizing the workshop content, including FAQs, maintenance tips, and troubleshooting common composting issues.
- Feedback Mechanism: Collect feedback from participants to gauge the effectiveness of the workshop and identify areas for improvement.
Engaging Schools and Local Organizations in Composting Initiatives
Schools and local organizations can play a pivotal role in promoting composting within communities. Engaging these groups can enhance participation and spread awareness. Strategies for involvement include:
- Curriculum Integration: Collaborating with educators to incorporate composting into science or environmental studies curricula fosters hands-on learning and green initiatives among students.
- Composting Clubs: Establishing composting clubs in schools or local organizations encourages peer-to-peer education and the development of leadership skills among participants.
- Community Challenges: Creating friendly competitions that encourage schools to achieve composting goals can boost engagement and foster a sense of community.
- Field Trips and Site Visits: Organizing trips to local composting facilities or successful community gardens provides students and community members with practical insights and inspiration.
- Recognition Programs: Implementing awards or recognition for schools and organizations that excel in composting initiatives motivates continuous participation and commitment.
Overcoming Common Misconceptions

Many people harbor misconceptions about composting, which can hinder their willingness to participate in this beneficial practice. Understanding these myths is essential to promoting composting effectively. Addressing these misunderstandings not only provides clarity but also inspires confidence in individuals who might be hesitant to start their own composting journey.A prevalent myth is that composting is a complicated and time-consuming process.
In reality, composting can be remarkably simple and requires minimal effort, especially if one starts small. Many individuals can begin with just a compost bin or even a designated corner in their backyard. By gradually introducing kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials, anyone can create nutrient-rich compost without feeling overwhelmed.
Common Myths About Composting
It is important to dismantle prevalent myths surrounding composting to encourage more people to engage in sustainable waste management practices. The following points highlight some of these misconceptions and provide factual corrections:
- Myth: Composting smells bad. In truth, when compost is managed properly—ensuring a balanced mix of greens (nitrogen-rich materials) and browns (carbon-rich materials)—there should be no foul odor. A well-maintained compost pile emits earthy, pleasant smells.
- Myth: Compost attracts pests. While it’s true that improperly managed compost can attract pests, a well-aerated and balanced compost pile minimizes this risk. Adding layers of browns and burying food scraps can help keep unwanted visitors at bay.
- Myth: You need a large space to compost. Composting can be done in small spaces, such as balconies or kitchens, using indoor compost bins or worm bins. Many urban dwellers successfully compost despite limited space.
Simplicity of Composting and Starting Small
Starting a composting habit can be an accessible endeavor for anyone interested in reducing waste and enhancing soil health. Beginners often find success by adopting straightforward practices that do not require extensive knowledge or resources. A simple approach is to collect organic scraps—like fruit peels, coffee grounds, and vegetable trimmings—in a designated container and eventually transferring them to a compost bin or pile.For those who desire to ease into composting, the following steps can guide their initial efforts:
- Choose a convenient location for a compost bin or pile, ensuring it is easily accessible.
- Begin by collecting kitchen scraps and yard waste, avoiding meat and dairy products to minimize odor and pest issues.
- Regularly turn the compost to promote aeration and speed up the decomposition process.
Environmental Impact of Composting vs. Traditional Waste Disposal
The environmental benefits of composting compared to traditional waste disposal methods are significant and far-reaching. Traditional waste disposal in landfills contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane, which is released during the anaerobic decomposition of organic materials. In contrast, composting manages organic waste through aerobic decomposition, resulting in a reduction in landfill contributions and a more sustainable approach to waste management.The comparison between these two methods can be summarized as follows:
- Composting reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Compost enriches soil health, improving its ability to retain moisture and nutrients while reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Traditional waste disposal lacks the ecological benefits of composting, leading to soil degradation and increased reliance on synthetic additives.
When more individuals understand these facts about composting and traditional waste management, it becomes easier to foster a culture of environmental responsibility and sustainable practices within communities.
Promoting Composting in Everyday Life

Incorporating composting into daily routines is an essential step toward a sustainable lifestyle. By making small adjustments, individuals can significantly reduce waste, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and enrich the soil in their gardens. Promoting composting not only benefits the environment but also encourages community involvement and a sense of shared responsibility toward our planet.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Composting
To effectively integrate composting into daily life, individuals can follow these practical tips:
- Designate a compost bin in the kitchen: Use a countertop compost bin to collect kitchen scraps such as fruit peels, vegetable trimmings, coffee grounds, and eggshells. This encourages daily composting habits.
- Start small: Begin with a manageable amount of waste. Gradually increase the quantity of compostable materials as you become more comfortable with the process.
- Be mindful of what goes into the compost: Focus on green materials (nitrogen-rich) such as grass clippings and kitchen scraps, alongside brown materials (carbon-rich) like dried leaves and cardboard.
- Set a routine: Establish a regular schedule for emptying the kitchen compost bin into an outdoor compost heap or bin to maintain freshness and prevent odors.
- Educate family members: Share the importance of composting with family, ensuring everyone understands which materials can be composted and how to properly contribute.
Creating a Compost Bin for Small Spaces
For those living in apartments or homes with limited outdoor space, creating a compost bin that fits within a small area is achievable. Consider the following options:
- Use a worm composting system (vermicomposting): This method utilizes red worms to break down organic waste in a compact bin, turning scraps into nutrient-rich fertilizer in a small footprint.
- Opt for a tumbling composter: These bins are designed to fit in small yards or patios and allow for easy mixing of compost materials, which accelerates the decomposition process.
- Implement a bokashi system: This method involves fermenting organic waste in an airtight container using beneficial microorganisms, making it suitable for indoor spaces.
Organizing a Community Composting Challenge
Engaging the community in composting can amplify its benefits and foster a sense of unity. Organizing a composting challenge can encourage participation and raise awareness. Key steps include:
- Set a clear objective: Define what the challenge aims to achieve, such as reducing waste by a certain percentage or increasing composting rates in the community.
- Promote the challenge through local events and social media: Create buzz by sharing information about the challenge, its benefits, and how residents can participate.
- Provide resources and workshops: Offer educational sessions on composting techniques, bin options, and acceptable materials to ensure participants feel equipped to succeed.
- Incentivize participation: Create friendly competitions among neighborhoods, rewarding those who achieve the most significant reduction in waste or create the best compost.
Case Studies and Success Stories
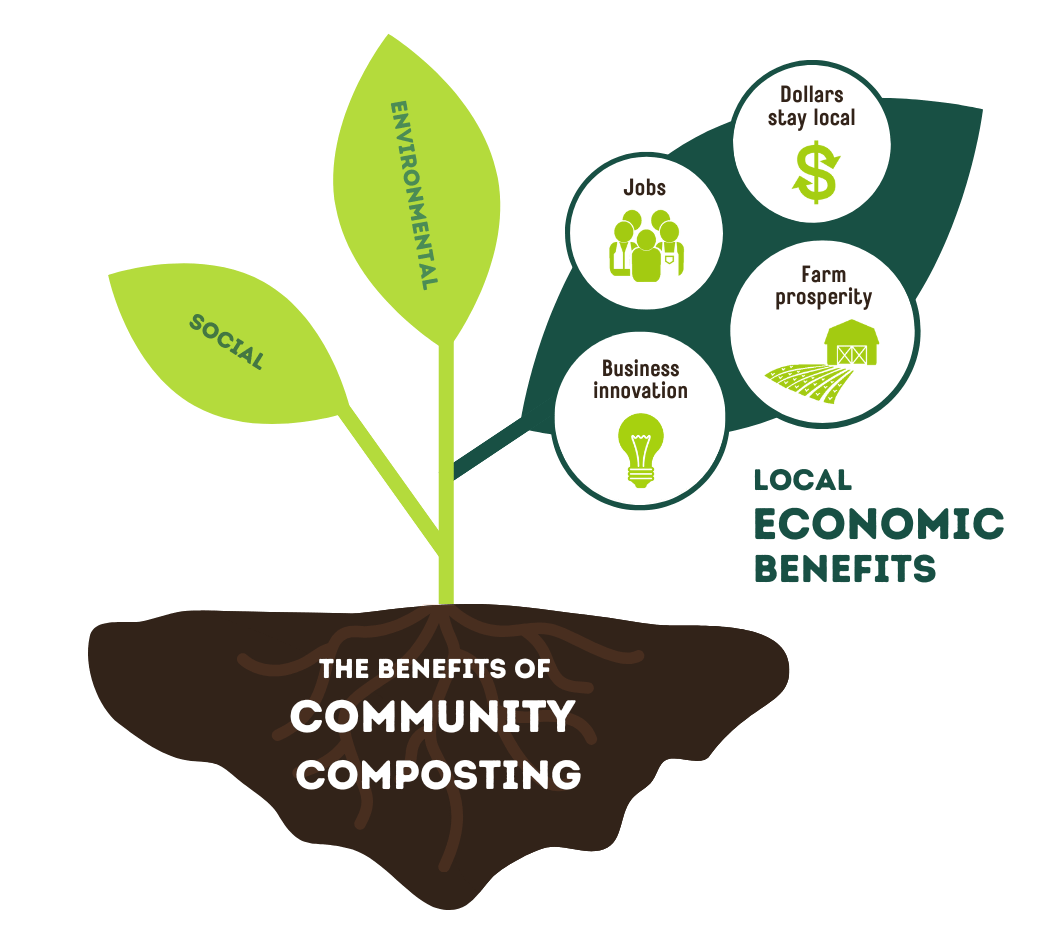
The adoption of composting practices has led to notable successes in various communities across the globe. By examining these case studies, we can gain a deeper understanding of how composting initiatives can transform environmental management and enhance community engagement. The following examples illustrate the tangible benefits of composting and the positive impacts it has had on local ecosystems, economies, and individual lifestyles.
Successful Composting Programs
Numerous regions have implemented successful composting programs that not only reduce waste but also promote sustainable practices within the community. These programs have demonstrated various positive outcomes, including improved soil health, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and increased community awareness about environmental responsibility. Highlighted below are several exemplary programs:
- San Francisco, California: The city of San Francisco has pioneered an ambitious composting initiative that mandates composting and recycling for all residents and businesses. As a result, the city has diverted over 80% of its waste from landfills, significantly reducing methane emissions, and enriching local soil with nutrient-dense compost.
- Toronto, Canada: Toronto’s green bin program encourages residents to compost organic materials. Since its inception, over one million households have participated, leading to the diversion of approximately 150,000 tonnes of organic waste annually. This program has contributed to lowering landfill use and improving soil quality in the region.
- Kerala, India: Kerala has embraced the concept of decentralized composting, allowing households to compost their organic waste at home. This initiative has empowered residents, reduced waste generation, and provided organic fertilizers for local agriculture. Community gardens have flourished as a direct result of this practice.
Positive Outcomes in Communities
Communities that have embraced composting initiatives have seen significant improvements in various aspects of life. The environmental benefits are complemented by social and economic advantages, which enhance community well-being. Examples of these outcomes include:
- Increased biodiversity: Composting enriches the soil, promoting healthy ecosystems that support diverse plant and animal life.
- Stronger local economies: By reducing waste disposal costs and providing valuable compost for agriculture, communities can stimulate local economies and promote sustainable agriculture practices.
- Increased community engagement: Composting initiatives often encourage collaboration among residents, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility for environmental stewardship.
Testimonials from Composting Practitioners
Personal experiences from individuals who practice composting highlight the numerous benefits of this sustainable practice. Testimonials often showcase not only the environmental advantages but also the personal satisfaction derived from participating in eco-friendly initiatives. Here are some insights from devoted composters:
“Composting has transformed my backyard into a thriving ecosystem. I’ve noticed healthier plants and reduced waste in my home. It’s incredibly rewarding to see the direct impact of my efforts.”
Sarah, Home Composter
“I never realized how much organic waste I was producing until I started composting. It feels great to know that I’m contributing to a healthier planet and reducing my carbon footprint.”
James, Community Gardener
“Participating in my city’s compost program has connected me with my neighbors, and we often share compost tips and gardening advice. It’s a great way to build community and promote sustainability!”
Linda, Urban Resident
These case studies and testimonials underscore the profound impact composting can have on individuals and communities alike, fostering environmental awareness and promoting sustainable living practices.
Closure
In summary, embracing composting offers a myriad of environmental benefits that extend beyond waste reduction to include improved soil health and water conservation. By addressing misconceptions and actively promoting composting within our communities, we pave the way for a sustainable future. As we share knowledge and experiences, we not only enhance our own practices but also empower others to partake in this rewarding endeavor, creating a ripple effect of positive change.